- Activiti6.0教程(1) - 环境搭建, 画一个流程图
- Activiti6.0教程(2) - 初始化表, 部署流程, 启动流程, 创建的表介绍
- Activiti6.0教程(3) - springboot项目中使用activiti6.0配置及启动
- Activiti6.0教程(4) - 任务的查询以及完成任务(对任务批注,以及对批注的查询)
- Activiti6.0教程(5) - 将任务的代理人配活(变量法, 监听法)
- Activiti6.0教程(6) - 排它网关/异或网关(ExclusiveGateway)用法
- Activiti6.0教程(7) - 并行网关(ParallelGateway)用法
- Activiti6.0教程(8) - 用户, 组, 用户与组关系用法
- Activiti6.0教程(9) - 候选任务, 在一个任务上设置多个候选人或候选组(根据实际业务指派给其中一个候选人执行)
官方文档描述
An exclusive gateway (also called the XOR gateway or more technical the exclusive data-based gateway), is used to model a decision in the process. When the execution arrives at this gateway, all outgoing sequence flow are evaluated in the order in which they are defined. The sequence flow which condition evaluates to true (or which doesn’t have a condition set, conceptually having a ‘true’ defined on the sequence flow) is selected for continuing the process.
Note that the semantics of outgoing sequence flow is different to that of the general case in BPMN 2.0. While in general all sequence flow which condition evaluates to true are selected to continue in a parallel way, only one sequence flow is selected when using the exclusive gateway. In case multiple sequence flow have a condition that evaluates to true, the first one defined in the XML (and only that one!) is selected for continuing the process. If no sequence flow can be selected, an exception will be thrown.
翻译过来就是
排它网关(也称为XOR网关或更技术的基于数据的排它网关)用于对流程中的决策进行建模。当执行到达此网关时,所有传出序列流都将按定义顺序进行计算。选
择条件计算结果为真(或没有条件集,概念上在序列流上定义了“真”)的序列流继续处理。
注意,传出序列流的语义不同于bpmn 2.0中的一般情况。通常情况下,条件值为true的所有序列流都选择以并行方式继续,但使用排它网关时只选择一个序列
流。如果多个序列流的条件的计算结果为true,则在XML中定义的第一个条件(并且只有该条件!)已选择继续该进程。如果无法选择序列流,则将引发异常。
说白了就是你传变量,网关帮你决定该走哪条线路, 下面说一下用法
流程图
首先它长这个样
我这画了个流程图, 大致流程就是 用户提交请假, 如果小于等于3天的由部门经理审批, 多于3天的要总经理审批
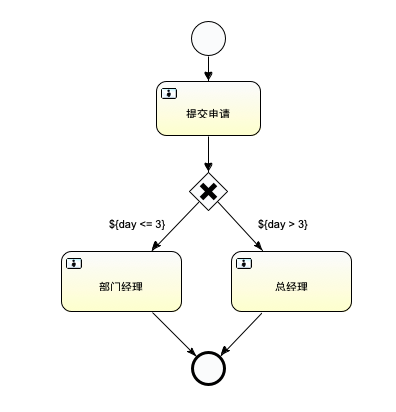
流程图里对应的代理人分别是
- 提交申请 user1
- 部门经理 user2
- 总经理 user3
测试
启动流程
@Test
public void startProcess() {
ProcessInstance instance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("TestExclusiveGateway");
System.out.println(instance.getId());
}
查询任务
原链接文:https://atjiu.github.io/2019/04/25/activiti-exclusive-gateway/
@Test
public void queryTask() {
List<Task> tasks = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskAssignee("user1")
// 分页查询
// .listPage(firstResult, maxResults)
// 排序
// .orderByTaskCreateTime().desc()
.list();
for (Task task : tasks) {
System.out.println("任务ID: " + task.getId());
System.out.println("代理人: " + task.getAssignee());
System.out.println("任务名: " + task.getName());
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
}
}
提交任务
注意user1提交申请的时候就要设置请假天数(day)这个变量了, 有了这个变量流程图的网关才会决定走哪条路
@Test
public void completeTask() {
String taskId = "18";
// 创建一个Map存放变量
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<>();
variables.put("day", 4);
// 处理任务
taskService.complete(taskId, variables);
}
我这测试设置的是4天, 数据库里任务的代理人就到user3了

后面处理流程就跟正常流程一样了
总结
这个网关的用处看网上有人说是能在流程图里处理的业务, 就不要写在代码里, 这样做有一定的安全性保障, 其实想想看, 一般流程图还不是程序员画的, 代码也是程序员写的, 安全性还不是程序员说的算 😂
写博客不易,转载请保留原文链接,谢谢!