之间整理过一篇 springboot 项目里使用 hibernate-validator 校验参数,然后在freemarker模板里取异常信息展示 的博客
现在都流行前后端分离了,服务端大都直接返json,又稍微折腾了一下,结合统一异常处理,优雅的实现请求参数的校验
创建项目
这个不多说,引入一个依赖即可
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.0.17.Final</version>
</dependency>
简单使用
使用 hibernate-validator 分两步
- 在controller类上加上
@Validated注解 - 在controller里方法的参数前加上相应的校验注解,比如
@NotNull
简单例子
import com.example.hibernatevalidator.util.Result;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
/**
* Created by tomoya at 2019/9/11
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
@Validated
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/index")
public Object index(@NotNull(message = "姓名不能为空") String name) {
return Result.success("你好," + name);
}
}
可以看到 @NotNull 注解是 javax.validation.constraints 这个包下的,后面介绍的一些校验注解都是这个包下的,可见hibernate-validator是实现的java的api
然后启动项目,浏览器访问 http://localhost:8080/index 可以看到出现了下面这个错误页面
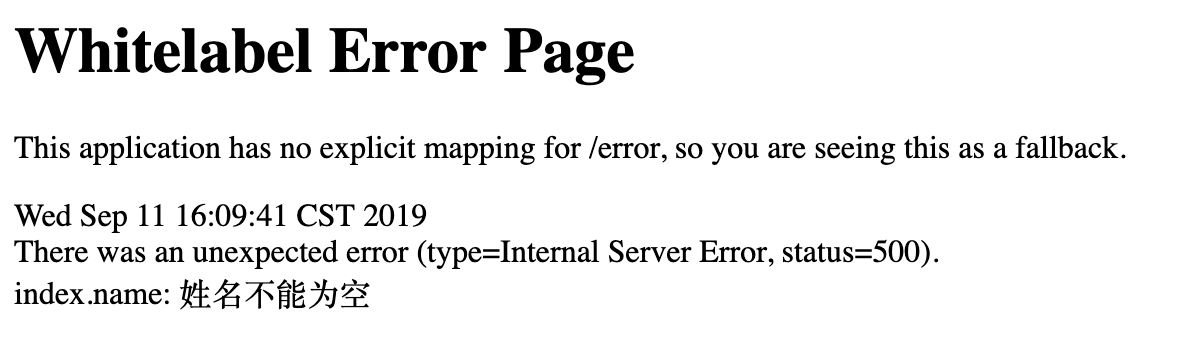
这个页面是springboot内置的错误页面
项目都前后端分离了,错误信息肯定最好也用json返回了,其实这时候如果用postman这样的工具来访问这个接口返回的就是一段json,长下面这个样
{
"timestamp": "2019-09-11T07:42:56.703+0000",
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"message": "index.name: 姓名不能为空",
"path": "/index"
}
就算是这个样也不是我想要的,项目里封装了一个类,专门返回json的,长这个样
public class Result {
private int code;
private String description;
private Object detail;
public static Result success(Object detail) {
Result result = new Result();
result.setCode(200);
result.setDetail(detail);
return result;
}
public static Result error(String description) {
Result result = new Result();
result.setCode(201);
result.setDescription(description);
return result;
}
// getter setter
}
怎么才能让hibernate-validator校验的异常信息以自己定义的类的格式返回呢?这就要用到统一异常处理了
链接文原: https://atjiu.github.io/2019/09/11/spring-boot-hibernate-validator-json/
统一异常处理
springmvc是相当的强大的,只需要两个注解就能使用统一异常处理 @ControllerAdvice 外加上 @ExceptionHandler
import com.example.hibernatevalidator.util.Result;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public Result defaultErrorHandler(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
return Result.error(e.getMessage());
}
}
这时候再用浏览器访问就可以看到返回的是一段json字符串了

常用校验注解
- @NotNull 只能判断是null的参数
- @NotBlank 可以判断null和空字符串
- @Email 校验参数是否是标准的email格式
- @URL 判断参数是否是一个正常的url地址
- @Max 判断一个数字最大值是多少,超过抛出异常
- @Min 与 @Max相反
- @Size 指定一个字符串的长度范围,包含最小和最大
- @Pattern 自定义正则校验参数
一个参数可以有多个校验注解来修饰
import com.example.hibernatevalidator.util.Result;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.validation.constraints.*;
/**
* Created by tomoya at 2019/9/11
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
@Validated
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/index")
public Object index(@NotBlank(message = "姓名不能为空") String name,
@NotNull(message = "age1不能为空") @Max(value = 12, message = "最大为12") Integer age1,
@NotNull(message = "age2不能为空") @Min(value = 6, message = "最小为6") Integer age2,
@NotNull(message = "address不能为空") @Size(min = 6, max = 20, message = "范围要在[6,20]之间") String address,
@NotNull(message = "password不能为空") @Pattern(regexp = "[a-zA-Z0-9]{4,16}$", message = "密码为字母+数字组合4-16位") String password) {
return Result.success("你好," + name);
}
}
访问浏览器 http://localhost:8080/index 输出的json长下面这个样
{
"code": 201,
"description": "index.address: address不能为空, index.age1: age1不能为空, index.password: password不能为空, index.age2: age2不能为空, index.name: 姓名不能为空"
}
异常分别处理
它是把错误信息都拼在一块输出的,这样在前端不好展示的,可以通过 : 和 , 将字符串分隔成前端想要的格式再返回,这个在统一异常处理那做就可以了
但这又会出一个问题,一个项目里用上了统一异常处理后,可不止校验这一个地方会出现异常,如果只是简单的使用 e.getMessage() 将异常信息拿出来进行分隔,肯定会出问题的,因为如果是空指针异常的话 e.getMessage() 取出来的是个null,这时候再进行 split() 肯定又会报错的
解决办法就是根据异常类来进行区分,通过断点可以发现 hibernate-validator 校验的异常类是 javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException
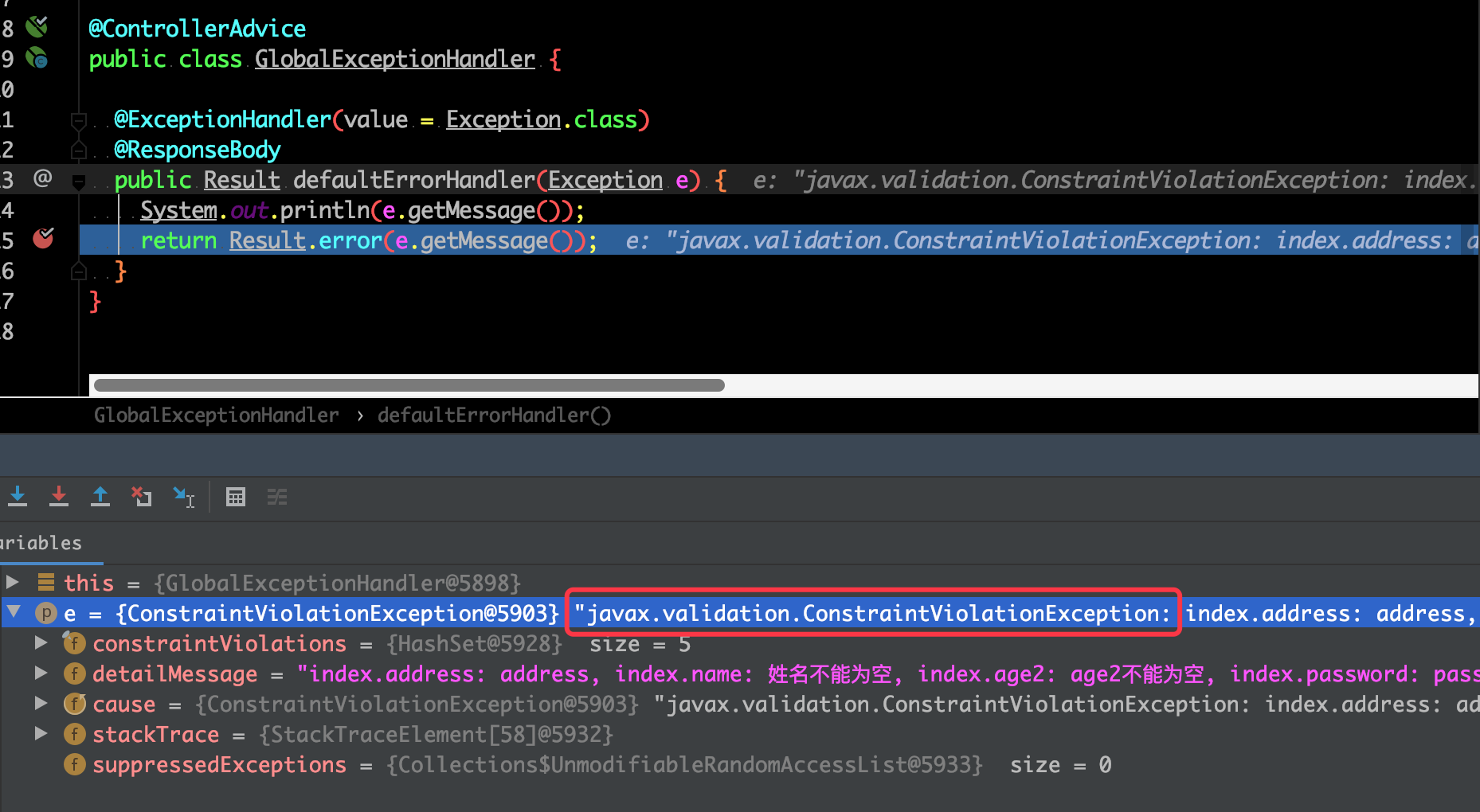
这样就可以做文章了,代码如下
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public Result defaultErrorHandler(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
if (e instanceof ConstraintViolationException) {
ConstraintViolationException constraintViolationException = (ConstraintViolationException) e;
String message = StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(
constraintViolationException.getConstraintViolations()
.stream()
.map(ConstraintViolation::getMessage)
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
return Result.error(message);
}
return Result.error("服务异常");
}
}
再次访问 异常信息就长下面这个样了
{
"code": 201,
"description": "age2不能为空,address不能为空,age1不能为空,password不能为空,姓名不能为空"
}
这只是一种分隔方法,可以自己定义自己的封装方式
对象校验
如果一个方法的参数相当的多,也可以将其封装在一个对象中,然后对这个对象进行校验,对象代码如下
文链接原: https://atjiu.github.io/2019/09/11/spring-boot-hibernate-validator-json/
import javax.validation.constraints.*;
/**
* Created by tomoya at 2019/9/11
*/
public class User {
@NotBlank(message = "姓名不能为空")
private String name;
@NotNull(message = "age1不能为空")
@Max(value = 12, message = "最大为12")
private Integer age1;
@NotNull(message = "age2不能为空")
@Min(value = 6, message = "最小为6")
private Integer age2;
@NotNull(message = "address不能为空")
@Size(min = 6, max = 20, message = "范围要在[6,20]之间")
private String address;
@NotNull(message = "password不能为空")
@Pattern(regexp = "[a-zA-Z0-9]{4,16}$", message = "密码为字母+数字组合4-16位")
private String password;
// getter setter
}
controller方法里参数也要换成对象,注解也变了
@GetMapping("/index1")
public Object index1(@Valid User user) {
return Result.success("你好," + user.getName());
}
访问浏览器,输出json如下
{
"code": 201,
"description": "服务异常"
}
这一看就不对,不是上面封装的异常处理信息,断点查看原来对对象进行校验异常类变成了 org.springframework.validation.BindException
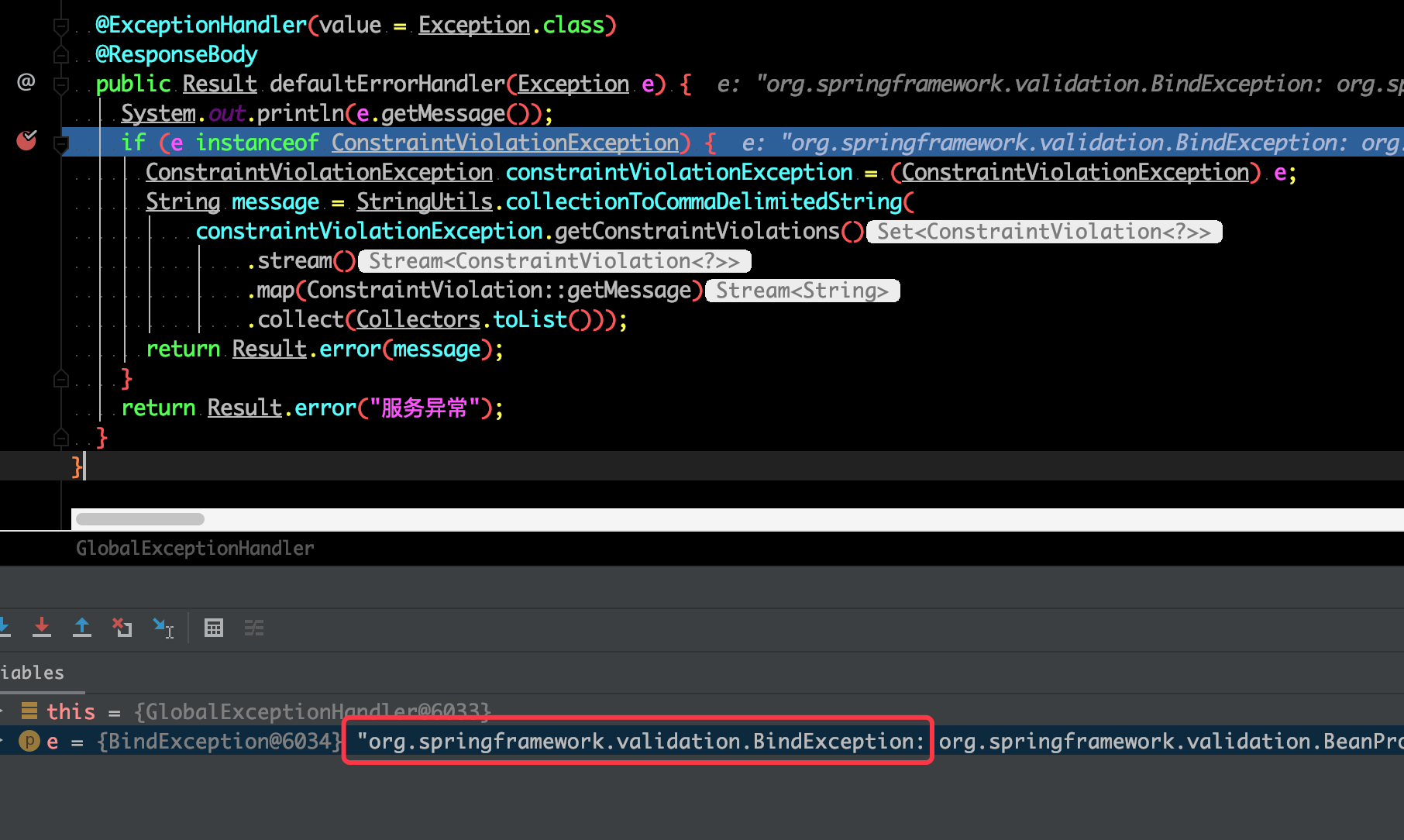
知道是哪个异常类就好办了,另外对这个异常类也做一下处理即可
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public Result defaultErrorHandler(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
if (e instanceof ConstraintViolationException) {
ConstraintViolationException constraintViolationException = (ConstraintViolationException) e;
String message = StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(
constraintViolationException.getConstraintViolations()
.stream()
.map(ConstraintViolation::getMessage)
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
return Result.error(message);
} else if (e instanceof BindException) {
BindException bindException = (BindException) e;
String message = StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(
bindException.getAllErrors()
.stream()
.map(DefaultMessageSourceResolvable::getDefaultMessage)
.collect(Collectors.toList())
);
return Result.error(message);
}
return Result.error("服务异常");
}
}
再次访问输出json
{
"code": 201,
"description": "姓名不能为空,age2不能为空,address不能为空,age1不能为空,password不能为空"
}
异常信息再次正常了
总结
hibernate-validator还是比较好用的,比在controller里一个参数一个参数的去判断要好看的多,但它也有个问题,如果一个请求方法里参数相当的多,就会想着去封装对象,这样看着也好看,但如果参数很多的方法非常多的话,就要多封装很多这样的对象,也就大大增加了项目中实体类的数量,这个我个人不太喜欢,所以不是太多的方法我一般都是直接写在controller方法的参数里的